حالیہ تجزیوں اور مطالعات نے بنی نوع انسان کو اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت سے بچانے کی امید پیدا کی ہے جو تیزی سے عالمی خطرہ بنتا جا رہا ہے۔
کی دریافت اینٹی بایوٹک in mid 1900s was a significant milestone in the history of medicine as it was a miracle therapeutic for many بیکٹیریل انفیکشن اور بیکٹیریا-causing diseases. اینٹی بایوٹک were once termed as a “wonder drug” and now antibiotics are indispensable in both basic healthcare and advanced medical care and technology as they have really changed the world by protecting lives and being an essential part of treating various medical conditions and asassisting in critical surgical procedures.
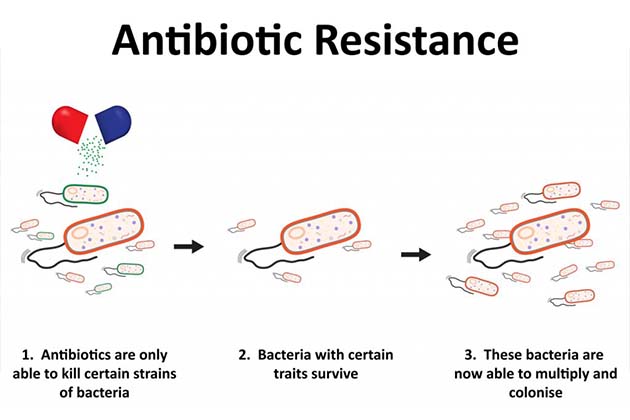
اینٹی بایوٹک کے خلاف مزاحمت تیز رفتاری سے بڑھ رہی ہے۔
اینٹی بایوٹک are medicines which are naturally produced by microorganisms and they stop or kill بیکٹیریا from growing. It is of critical importance because بیکٹیریل infections have plagued mankind throughout time. However, “resistant” بیکٹیریا develop defences that protect them against the effects of اینٹی بایوٹک when previously they were killed by them. These resistant bacteria then are able to withstand any attacks by antibiotics and consequently if these بیکٹیریا are disease-causing standard treatments stop working for that disease persisting the infections which can then easily spread to others. Thus, the “magical” antibiotics have unfortunately started to fail or started becoming ineffective and this is posing immense threat to the healthcare system worldwide. The number of resistant بیکٹیریا already cause more than 500,000 deaths every year and are eroding the efficiency of antibiotics for prevention and cure by being a silent killer by residing in almost 60% of the world’s populations in some form. اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت threatens our ability to cure many diseases like tuberculosis, pneumonia and carry out advances in surgeries, treatment of cancer etc. It is estimated that approximately 50 million people will die from antibiotic resistant infections by 2050 and the day might actually come when اینٹی بایوٹک can no longer be used for treating critical infections the way they are being used now. This issue of antibiotic resistance is now an important health topic which needs to be addressed with a sense of urgency for a better future and the medical and scientific community and the governments worldwide are taking several steps toward achieving this goal.
ڈبلیو ایچ او سروے: 'اینٹی بائیوٹک کے بعد کا دور'؟
ورلڈ ہیلتھ آرگنائزیشن (ڈبلیو ایچ او) نے اعلان کیا ہے۔ اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت اس کے گلوبل اینٹی مائکروبیل ریزسٹنس سرویلنس سسٹم (GLASS) کے ذریعے ایک اعلی ترجیحی اور سنگین صحت کا مسئلہ جو اکتوبر 2015 میں شروع کیا گیا تھا۔ یہ نظام دنیا بھر میں اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت پر ڈیٹا اکٹھا، تجزیہ اور شیئر کرتا ہے۔ 2017 تک، 52 ممالک (25 اعلی آمدنی والے، 20 درمیانی آمدنی والے اور سات کم آمدنی والے ممالک) نے GLASS میں داخلہ لیا ہے۔ یہ پہلی رپورٹ ہے۔1 22 ممالک (سروے میں شامل ڈیڑھ ملین شرکاء) کی طرف سے فراہم کردہ اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت کی سطح کے بارے میں معلومات پر مشتمل ہے جو خطرناک شرح سے نمو دکھا رہی ہے – مجموعی طور پر 62 سے 82 فیصد مزاحمت۔ ڈبلیو ایچ او کے اس اقدام کا مقصد عالمی سطح پر اس سنگین مسئلے سے نمٹنے کے لیے مختلف ممالک کے درمیان آگاہی اور ہم آہنگی پیدا کرنا ہے۔
ہم اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت کو روک سکتے تھے اور اب بھی کر سکتے ہیں۔
How did we reach this phase of humanity where antibiotic resistance has turned into a global threat? The answer to that is quite simple: we have extremely overused and misused اینٹی بایوٹک. The doctors have overly prescribed اینٹی بایوٹک to any or every patient in the past many decades. Also, in many countries, especially the developing countries of Asia and Africa, اینٹی بایوٹک are available over-the-counter at the local pharmacist and can be purchased without even requiring a doctor’s prescription. It is estimated that 50 percent of the time اینٹی بایوٹک are prescribed for virus-causing infection where they basically do no good because the virus will still complete its life span (generally between 3-10 days) whether اینٹی بایوٹک are taken or not. In fact, it’s just incorrect and a mystery for many as to how exactly اینٹی بایوٹک (which target بیکٹیریا) will have any effect on viruses! The اینٹی بایوٹک could ‘maybe’ relieve some symptoms associated with the viral infection. Even then this continues to be medically unethical. The correct advice should be that since no treatment is available for most viruses, the infection should just run its course and in the future these infections should be alternatively prevented by following strict hygiene and keeping one’s environment clean. Furthermore, اینٹی بایوٹک are being routinely used in enhancing agricultural output worldwide and feeding to livestock and food-producing animals (chicken, cow, pig) as growth supplements. By doing so humans are also put to huge risk of ingesting antibiotic-resistant بیکٹیریا which reside in those food or animals causing rigorous transfer of resistant strain بیکٹیریا سرحدوں کے اس پار۔
یہ منظر نامہ اس حقیقت سے مزید پیچیدہ ہے کہ پچھلی کئی دہائیوں میں فارما کمپنیوں کی جانب سے کوئی نئی اینٹی بائیوٹک تیار نہیں کی گئی ہے - گرام منفی کے لیے آخری نئی اینٹی بائیوٹک کلاس۔ بیکٹیریا quinolones چار دہائیوں پہلے تیار کیا گیا تھا. اس طرح، جیسا کہ ہم اس وقت کھڑے ہیں، ہم واقعی روکنے کے بارے میں سوچ نہیں سکتے اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت زیادہ سے زیادہ مختلف اینٹی بائیوٹکس شامل کرنے سے کیونکہ یہ صرف مزاحمت اور منتقلی کو مزید پیچیدہ کرے گا۔ بہت منشیات کی کمپنیوں نے نشاندہی کی ہے کہ کسی بھی نئے کی ترقی منشیات کی سب سے پہلے بہت مہنگا ہے کیونکہ یہ ایک طویل عمل ہے جس میں بھاری سرمایہ کاری اور ممکنہ منافع کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے۔ اینٹی بایوٹک is generally very low that the companies are unable to ‘break even’. This is convoluted by the fact that a resistant strain would develop for a new antibiotic somewhere in the world within two years of its launch since no legal framework is in place to curb antibiotic overuse. This doesn’t exactly sound hopeful from a commercial as well as a medical point of view and thus developing new اینٹی بایوٹک is not the solution for prevention of their resistance.
ڈبلیو ایچ او ایکشن پلان کی سفارش کرتا ہے۔2 اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت کو روکنے کے لیے:
a) Healthcare professionals and workers should be doing a careful detailed assessment before prescribing اینٹی بایوٹک to humans or animals. A Cochrane review of various methods3 aimed at reducing antibiotic abuse in any clinical set up has concluded that the ‘3-day prescription’ method was fairly successful, in which the patient suffering from an infection (which is not بیکٹیریل) is conveyed that his/her condition will improve in 3 days, else اینٹی بایوٹک can be taken if symptoms get worse – which generally don’t since the viral infection has run its course by that time. b) The general public should be confident to ask questions when they are being prescribed اینٹی بایوٹک and they must take اینٹی بایوٹک only when satisfied that it is absolutely necessary. They must also complete the prescribed dosage to prevent fast growth of resistant بیکٹیریل strains. c) Agriculturists and livestock breeders should follow a regulated, limited use of antibiotics and do so only where it matters (eg. to treat an infection). d) Governments should setup and follow national level plans to curb antibiotic use1. ترقی یافتہ ممالک اور متوسط اور کم آمدنی والے ممالک کے لیے ان کی ضروریات سے متعلق اپنی مرضی کے مطابق فریم ورک قائم کرنے کی ضرورت ہے۔
اب جب کہ نقصان ہو چکا ہے: اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت سے نمٹنا
So that we do not plunge into a new ’post اینٹی بایوٹک’ era and return to the pre-penicillin (first antibiotic to be discovered) era, lot of research is happening in this field loaded with failure and occasional successes. Recent multiple studies show ways to tackle and maybe reverse antibiotic resistance. The first study published in جرنل آف اینٹی مائکرو کیمیکل کیموتھریپی4 ظاہر کرتا ہے کہ جب بیکٹیریا become resistant, one of the ways which they adopt to restrict اینٹی بایوٹک action is by producing an enzyme (a β-lactamase) which destroys any antibiotic that is trying to get into the cell (for treatment). Thus, ways to inhibit the action of such enzymes could successfully reverse antibiotic resistance. In a second subsequent study from the same team at University of Bristol, UK but in collaboration with University of Oxford published in آلودگی مائکروبالوجی5, they analysed the effectiveness of two types of inhibitors of such enzymes. These inhibitors (from the bicyclic boronate class) were seen to be very effective on a particular type of antibiotic (aztreonam) such that in the presence of this inhibitor, the antibiotic was able to kill many resistant بیکٹیریا. Two of such inhibitors avibactam and vaborbactam – are now undergoing clinical trial and have been able to save a life of a person suffering from untreatable infection.The authors have succeeded with only a particular type of اینٹی بائیوٹکاس کے باوجود، ان کے کام نے اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت کی لہر کو واپس کرنے میں امید پیدا کی ہے۔
میں شائع ہونے والی ایک اور تحقیق میں سائنسی رپورٹیں6, Université de Montréal کے محققین نے بیکٹیریا کے درمیان مزاحمت کی منتقلی کو روکنے کے لیے ایک نیا طریقہ وضع کیا ہے جو کہ ہسپتالوں اور ہیلتھ یونٹس میں اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت کے پھیلاؤ کے طریقوں میں سے ایک ہے۔ بیکٹیریا کو مزاحم بنانے کے لیے ذمہ دار جینز کو پلاسمیڈ (ایک چھوٹا سا DNA ٹکڑا جو آزادانہ طور پر نقل کر سکتا ہے) اور یہ پلازمیڈ بیکٹیریا کے درمیان منتقل ہو جاتے ہیں، اس طرح مزاحم کو پھیلاتے ہیں بیکٹیریا دور دور تک محققین نے کمپیوٹیشنل طور پر چھوٹے کیمیائی مالیکیولز کی ایک لائبریری کی اسکریننگ کی جو پروٹین (TraE) سے جڑے ہوں گے جو اس پلاسمڈ کی منتقلی کے لیے ضروری ہے۔ روکنے والے بائنڈنگ سائٹ کو پروٹین کے 3D مالیکیولر ڈھانچے سے جانا جاتا ہے اور یہ دیکھا گیا تھا کہ ایک بار ممکنہ روکنے والے پروٹین کے ساتھ جڑے ہوئے تھے، اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحم، جین لے جانے والے پلاسمڈ کی منتقلی میں نمایاں کمی واقع ہوئی تھی اس طرح اینٹی بائیوٹک کو محدود کرنے اور ریورس کرنے کے لیے ممکنہ حکمت عملی تجویز کی گئی تھی۔ مزاحمت تاہم، مطالعہ کے اس قسم کے لئے 3D ایک پروٹین کی سالماتی ساخت کی ضرورت ہوتی ہے جس کی وجہ سے یہ قدرے محدود ہوجاتا ہے کیونکہ بہت سے پروٹینوں کی ساختی خصوصیات ہونا باقی ہیں۔ اس کے باوجود، خیال حوصلہ افزا ہے اور اس طرح کے روکنے والے ممکنہ طور پر روزمرہ کی صحت کی دیکھ بھال میں اہم کردار ادا کر سکتے ہیں۔
اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت کئی دہائیوں کی بہتری اور کامیابیوں کو خطرہ اور نقصان پہنچا رہی ہے جو انسانوں میں کی گئی ہیں۔ صحت کی دیکھ بھال اور ترقی and implementation of this work will have a huge direct impact on the capability of people to live healthy lives.
***
{آپ اصل تحقیقی مقالے کو ذیل میں دیے گئے DOI لنک پر کلک کر کے پڑھ سکتے ہیں جو حوالہ دیئے گئے ماخذ کی فہرست میں ہے}
ذرائع)
1. ڈبلیو ایچ او۔ عالمی antimicrobial ریزسٹنس سرویلنس سسٹم (GLASS) رپورٹ۔ http://www.who.int/glass/resources/publications/early-implementation-report/en/ [29 جنوری 2018 تک رسائی حاصل کی گئی]۔
2. ڈبلیو ایچ او۔ اینٹی بائیوٹک مزاحمت کو کیسے روکا جائے؟ یہاں WHO کا نسخہ ہے۔ http://www.who.int/mediacentre/commentaries/stop-antibiotic-resistance/en/. [10 فروری 2018 تک رسائی حاصل کی]۔
3. آرنلڈ ایس آر۔ اور Straus SE. 2005. ایمبولیٹری کیئر میں اینٹی بائیوٹک تجویز کرنے کے طریقوں کو بہتر بنانے کے لیے مداخلتیں۔Cochrane ڈیٹا بیس Syst Rev. 19(4)۔ https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD003539.pub2
4. Jimenez-Castellanos JC۔ ET رحمہ اللہ تعالی. 2017. کلیبسیلا نمونیا میں رام اے کی زیادہ پیداوار سے چلنے والی لفافے پروٹوم تبدیلیاں جو حاصل شدہ β-لیکٹم مزاحمت کو بڑھاتی ہیں۔ جرنل آف اینٹی مائکرو کیمیکل کیموتھریپی. 73(1) https://doi.org/10.1093/jac/dkx345
5. Calvopiña K. et al.2017. بڑے پیمانے پر منشیات کے خلاف مزاحم Stenotrophomonasmaltophilia کلینکل الگ تھلگوں کے خلاف نان کلاسیکل β-lactamase inhibitors کی افادیت کے بارے میں ساختی/میکانیاتی بصیرت۔ مالیکیولر مائکرو بایولوجی۔ 106(3)۔ https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.13831
6. Casu B. et al. 2017. فریگمنٹ پر مبنی اسکریننگ پلازمڈ pKM101 کے ذریعے antimicrobial مزاحمت کی conjugative منتقلی کے روکنے والوں کے لیے نئے اہداف کی نشاندہی کرتی ہے۔ سائنسی رپورٹیں. 7(1)۔ https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-14953-1